Utah IRM at a glance
With the Utah release, new features and enhancements have been made within the following areas:
Common Control Management
Issue Management
Risk Appetite framework
Operational Resilience Workspace
1. Common Control Management
Policy & Compliance and Risk Management
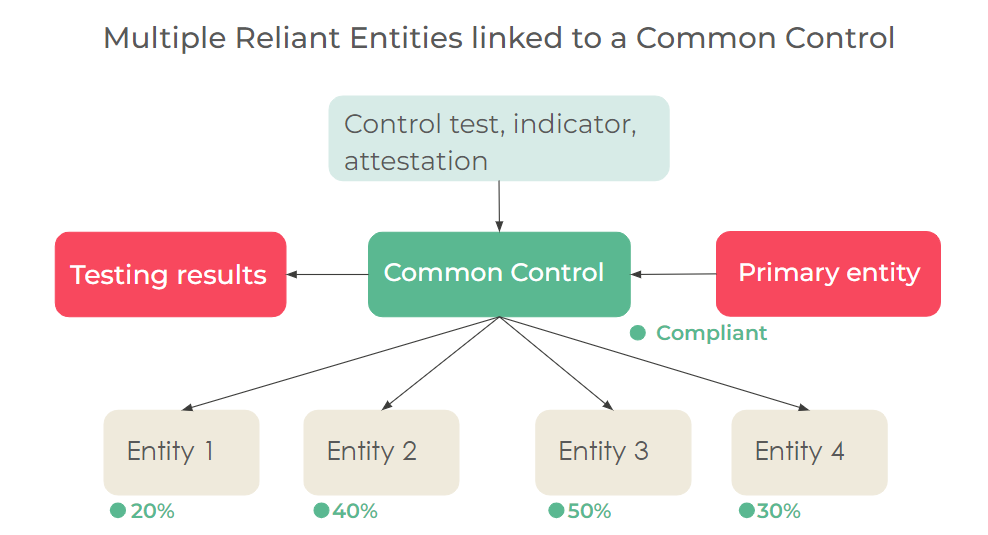
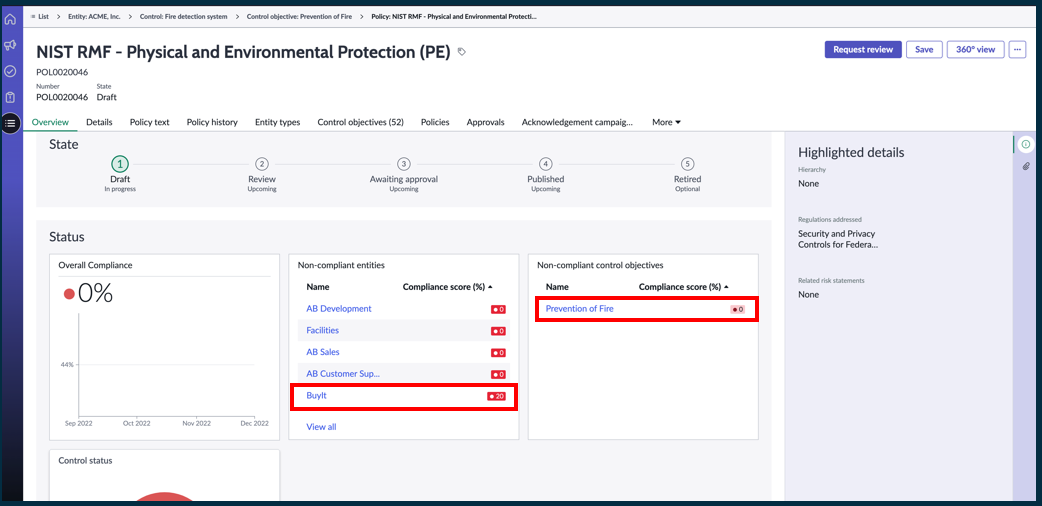
Add or remove the reliant entity association of the common controls to a primary entity with the new ‘Downstream inherited controls’ related list. This list is added to the Entity form. You can also see the directly related inherited controls in this related list. The 360-degree view of the entity shows both the controls and inherited controls.
- Provide customers with the capability to test and certify control once and have it be inherited by many.
- Users can now create a common control that can be linked to multiple entities to reduce the number of controls that must be maintained.
- Improving efficiency, reducing time and effort required in the management of such controls.
- Common controls can inherit control testing results, for the primary entity, to all linked entities for risk identification, audit, and compliance purposes – reducing the time and cost of control testing.
The business outcome is to save time and effort by reducing unnecessary control testing. Hiring skilled talent is a challenge, so GRC teams are overworked. Additionally, organisations are once again looking to optimise operations to reduce costs. Reducing unnecessary or redundant work reduces the workload on GRC teams, improves job satisfaction and reduces costs as productivity and efficiency increase.
Customer benefits
Currently, the process requires all application owners to attest such controls individually, which creates inefficiency and redundancy in the system.
The new process of Common Control is assigned to a primary entity. The control status and testing results are inherited by other entities that rely on the primary entity.
- Reduced number of controls: Create a common control that can be linked to multiple entities to reduce the number of controls that must be maintained.
- Inherit control testing results of common control, for primary entities, to all linked entities for risk identification, audit, and compliance purposes
- Reduced time and effort: Testing once and applying to many helps with reducing the time and effort associated with how controls are implemented within an organisation/environment, as new systems are deployed and pre-validation audits take place.
- Share work: Provides an opportunity to share work that has already been done to save others the time and effort needed to properly document the controls for their systems or entities.
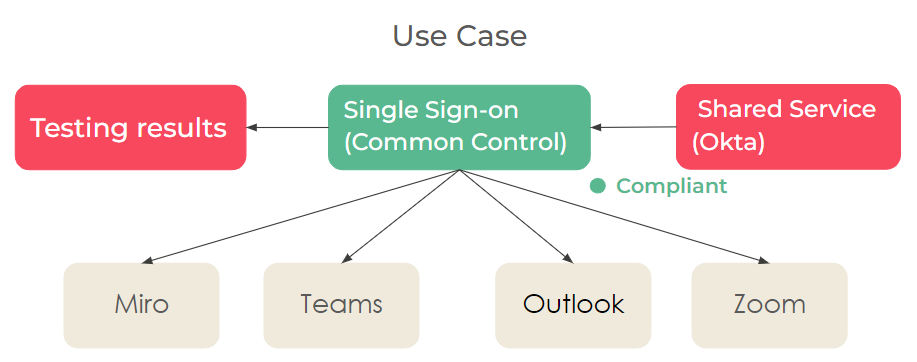
Use case
A single sign-on for business applications basically relies on IAM solutions and doesn’t need to have application owners held accountable for it, as such controls are managed by a shared service. Currently, the process requires all application owners to attest such controls individually which creates inefficiency and redundancy in the system.
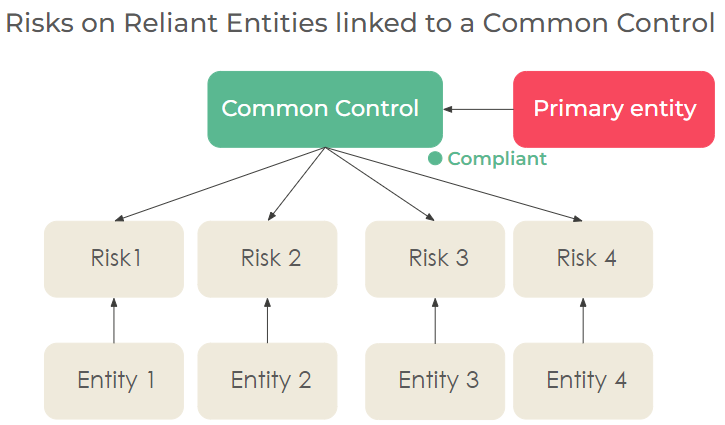
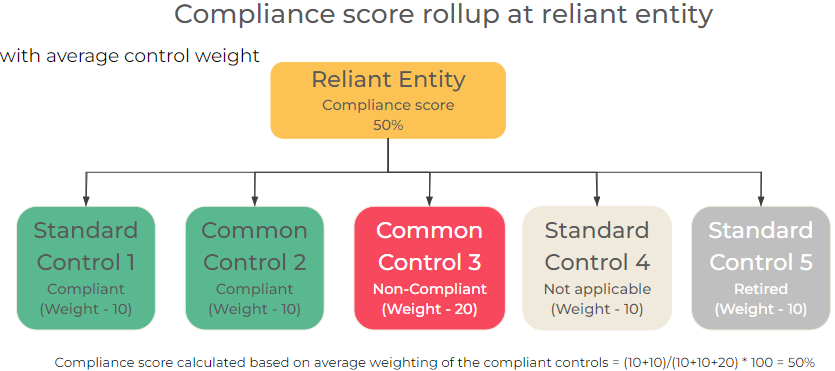
Common control creation constraints
When the existence of common controls or associations of reliant entities to common control or standard controls are checked, the control’s name, entity and control objective should exactly match.
The order of precedence between standard and common controls is as follows:
- Based on the action type, a standard control would be created, if a reliant association or standard control both don’t exist (e.g.: Add control objective to entity type, Add a policy to entity type, Activate control objective, Activate policy).
- Based on the action type, a reliant association to common control would be created if a reliant association or standard control both don’t exist (e.g.: Add entity type to common control)
- In the case of conflicting entity type, where a standard control does not already exist, but a common one does, preference would always be given to the association of a reliant entity to the common control over the creation of a standard control (e.g.: Add the entity to entity type).
What’s new in Reports in the workspace
Entity
Entity overview: New widgets ‘Inherited controls’ and ‘Highlighted details’ have been added for common controls.
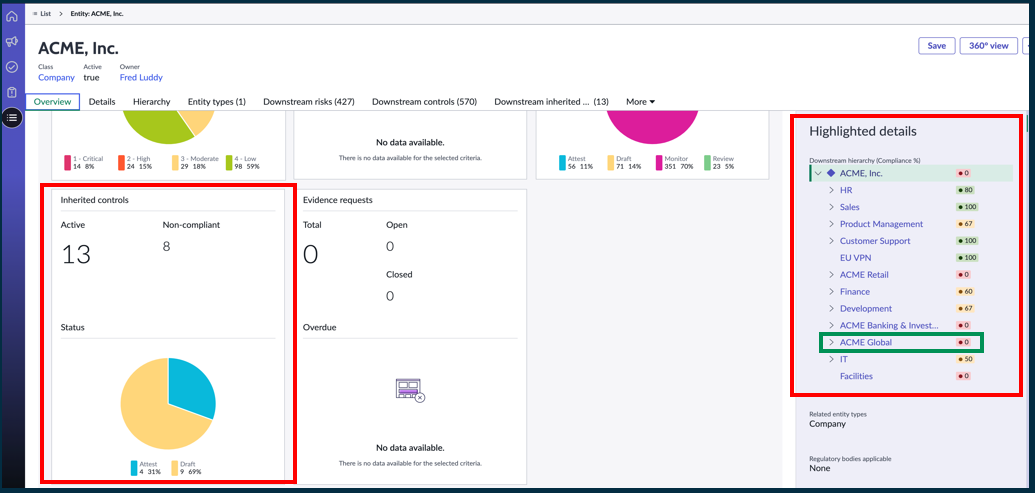
Common Control
Reliant entities have been added on the side panel of the control.
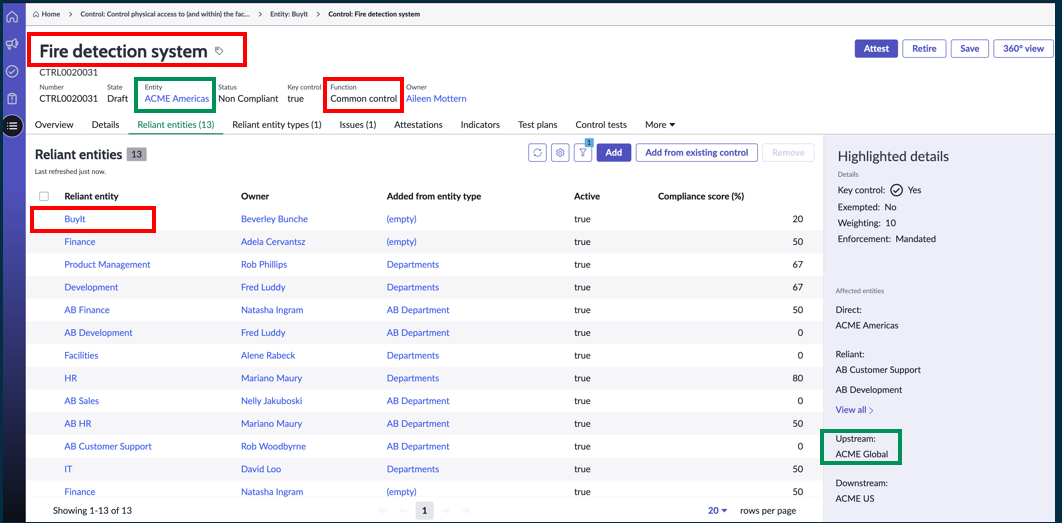
Common control – Reliant Entities on a 360-degree view
The entire relationship for a selected control, such as the upstream Control objectives, controls, open issues and entities that are associated with the control.
Policy
The widget ‘Non-compliance entities’ now includes ‘Reliant Entities’.
2. Issue Management
Common Core
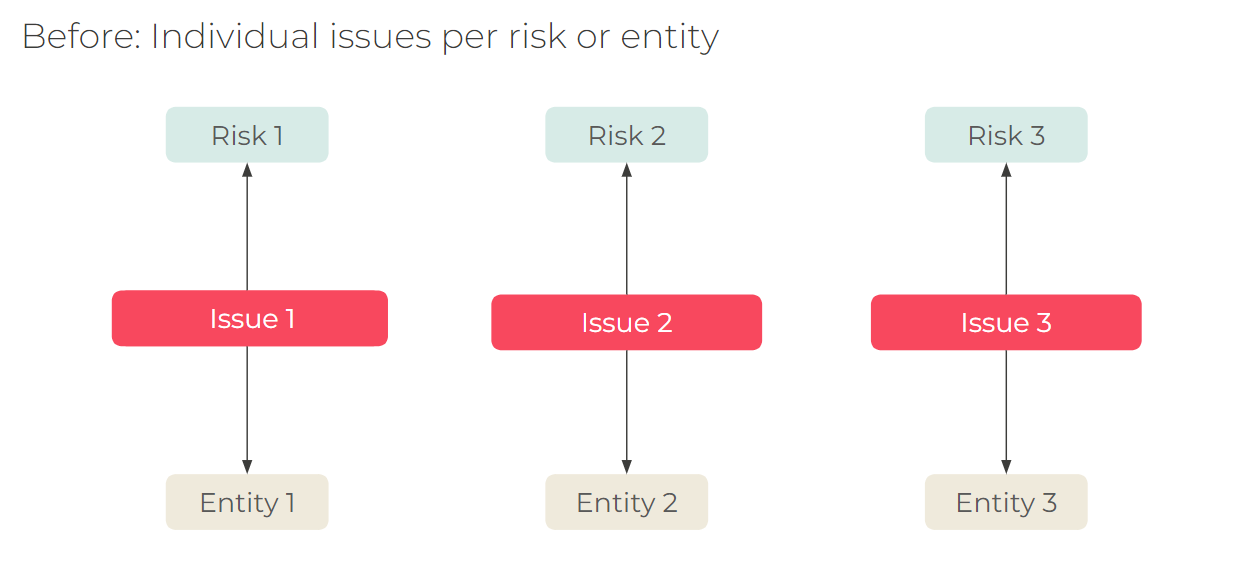
Reuse the same issue by associating it with different objects. When an issue is linked to a control or risk, it’s automatically linked to the control objective or risk statement with its associated entity.
Issue data model
- Provides customers with the ability to relate issues to multiple risks/controls etc., enabling better impact analysis and reuse of issues.
- Significantly reduces the effort and time required for the customers in managing issues at scale within the organisation, as well as enables a more effective assessment of the impact of the issue.
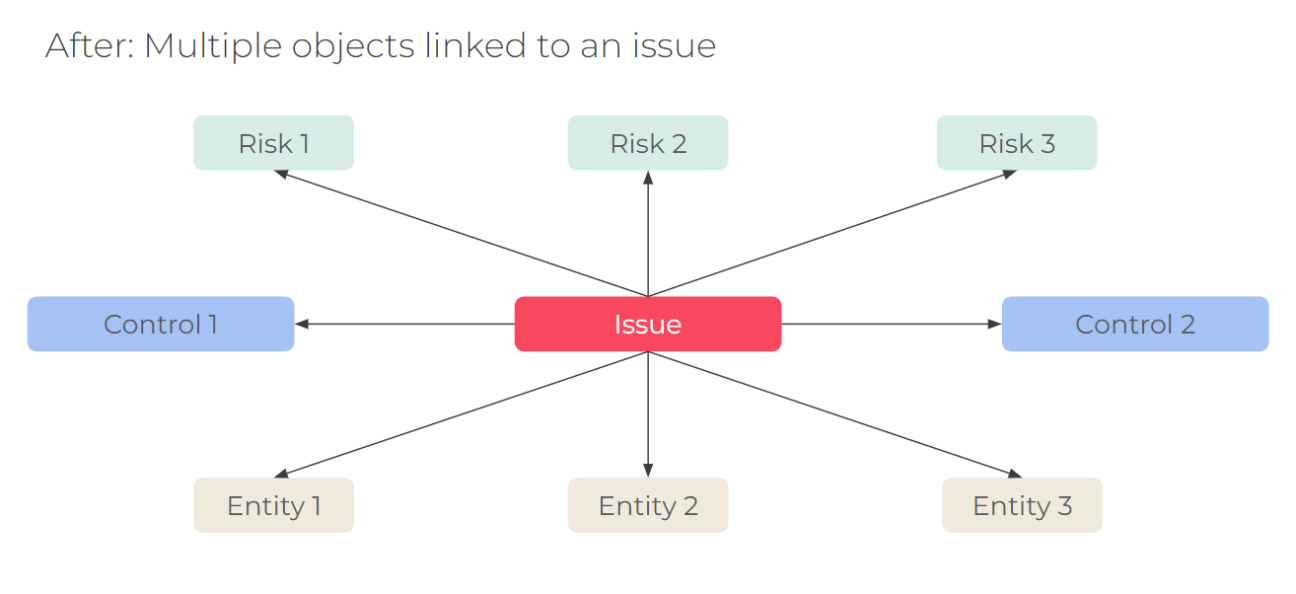
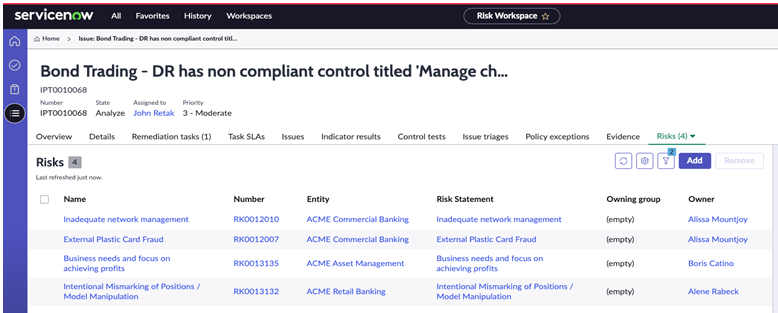
- A single issue can now be linked to multiple risks, controls, entities, and other objects to eliminate duplicate issues.
- Fewer issues that present a more holistic view of the impacted controls, engagements, risk events, and other sources simplify audit.
- You can now tag an issue to multiple sources of failure (e.g. multiple controls) to improve risk tracking and analysis.
The business outcome is to increase efficiency with simplified issue management. Organisations need to be able to do more with less: not just because of a lack of skilled talent, but also because of the pressure to optimise operations and reduce costs. Reducing the number of issues that Risk or Compliance teams or control owners must create, track, analyse, respond to, and close could save significant time and money.
Increase efficiency with simplified issue management
- Reduce the number of issues: Create a single issue that can link to multiple risks, controls, entities, and other objects (see the related list on the issue form and side panel) to eliminate duplicate issues.
- Reduce time and effort: Relinking the same issue with multiple Risks and controls by reducing the time and effort associated with creating individual duplicate issues per control and risk when the root cause identified is the same.
- Share work: Provides an opportunity to share work that has already been done to save others’ time and effort needed to properly document the issue per controls for their system and entities.
- Simplify audit with fewer issues that present a holistic view of the impacted controls, engagements, risk events, and other sources
- Tag an issue to multiple sources of failure (e.g. multiple controls) to improve risk tracking and analysis
New Issue form – Fields moved to related records
- All reference fields on issue forms are now available as a related list for ease of access.
- This will also allow linking multiple objects to the same issue.
- Updated the side panel to showcase related records.
- The Issue Configuration module is available for admins to auto-populate related records. E.g., when a risk is related to an issue, the entity associated with the risk will also get linked to the issue.
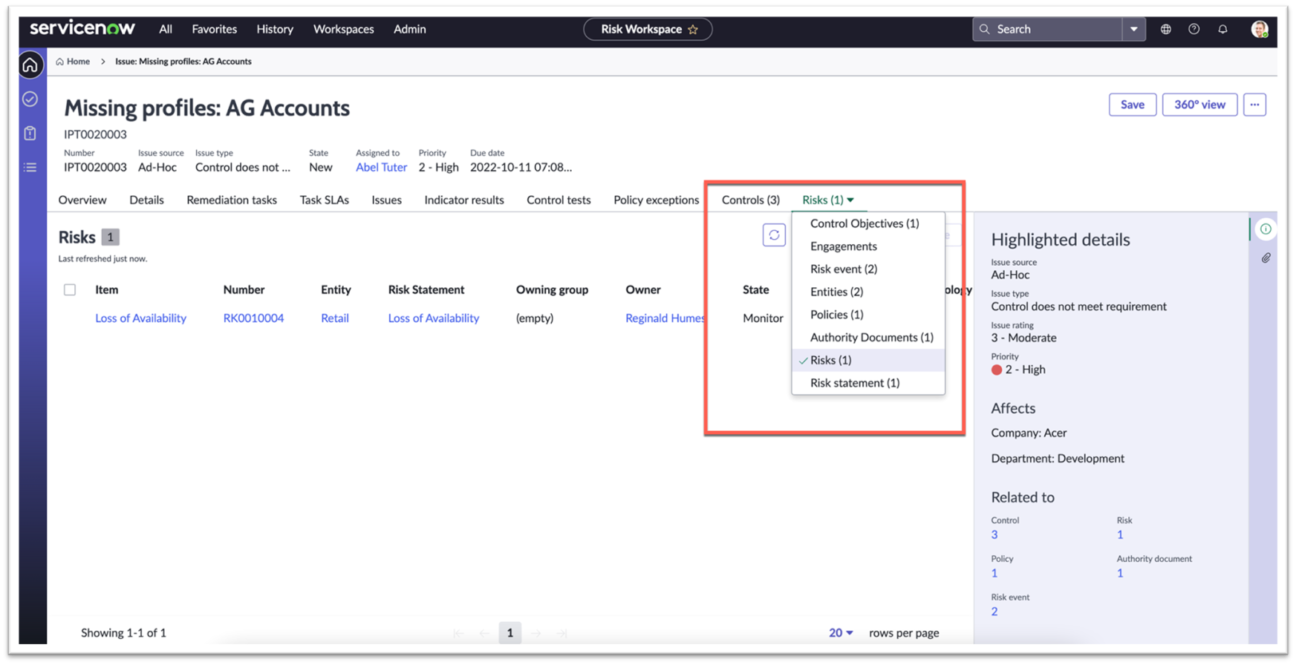
New Issue form – Option to add/remove
Add or remove risks, controls, entities, and other objects.
- Automatically adds a Risk statement and entities when a new Risk is added.
- Automatically adds a Control Objective and entities when a new Control is added.
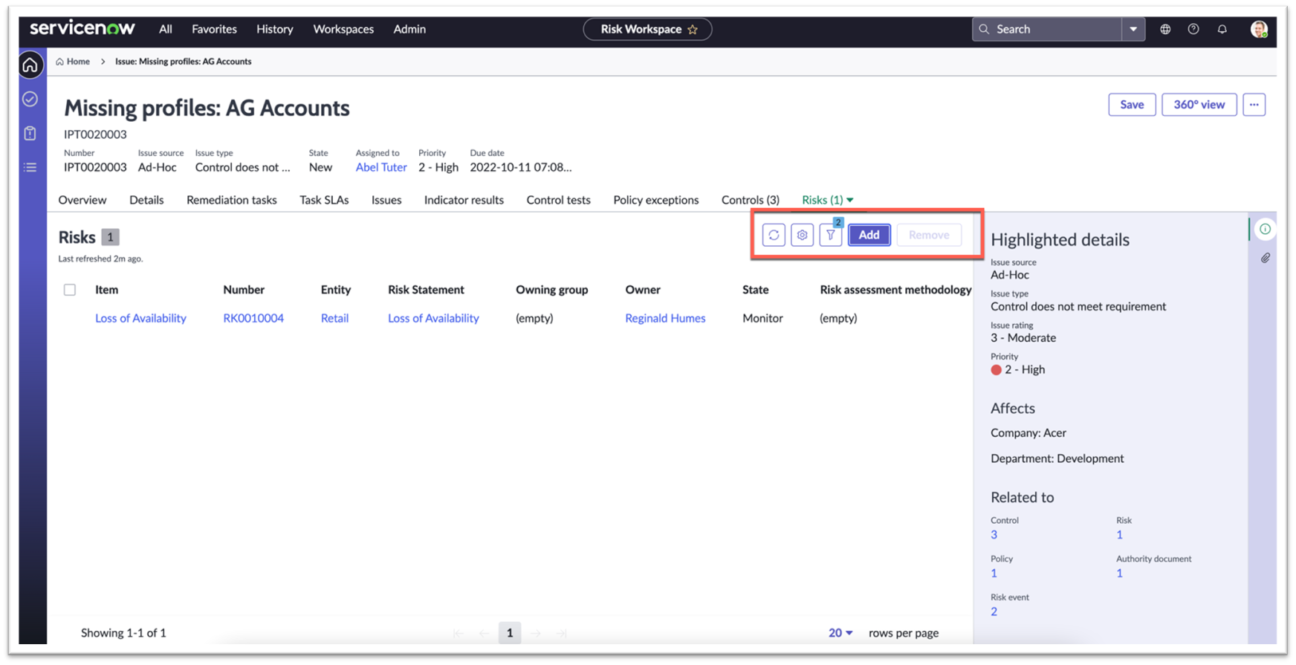
The automation is done by the Issue Configuration module where you can configure new m2m relationships.

New Issue form – Now select multiple records
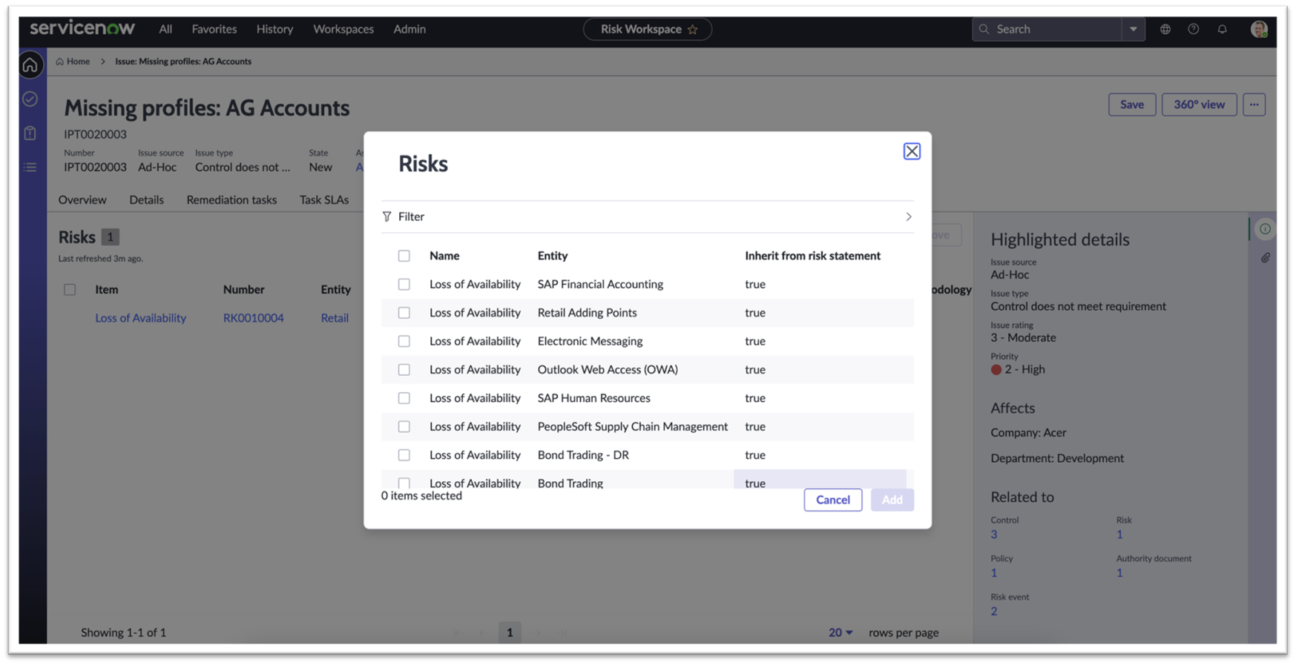
New Issue form – Updated side panel
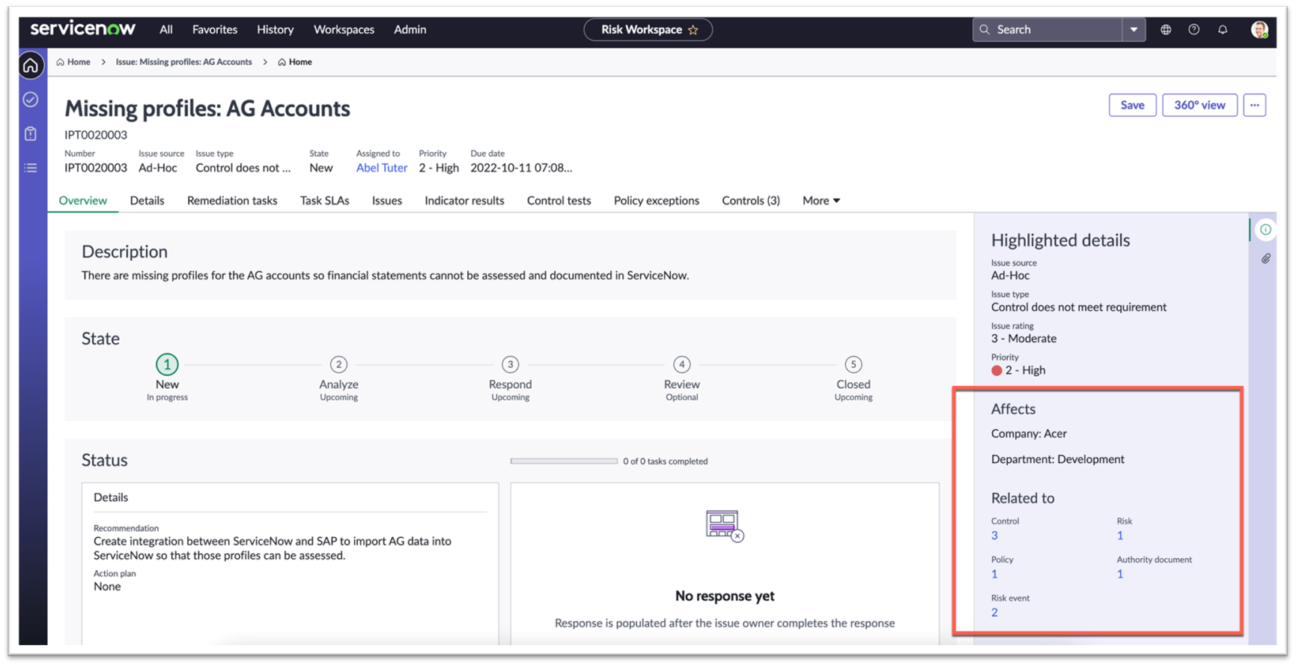
An issue can be related to multiple risks
3. Risk Appetite Frameworks
Risk Management
Risk Appetite is the amount of risk that an organisation is ready to take in order to achieve its strategic objectives. It sets a clear strategic direction and a tolerance in the pursuit of earnings, adequate capital and shareholder value.
In simple words, they are “boundaries for making decisions”. The board is responsible for making sure that the monitoring and internal controls of the company are such that the firm operates within its Risk Appetite.
Defining a Risk Appetite means assessing all possible risks and establishing boundaries for acceptable and unacceptable risks.
Once the Risk Appetite is defined, the risk function is responsible for monitoring risk exposure and ensuring it is consistent with the Risk Appetite, and raising challenges against unacceptable risks.
The goal is to provide a decision-making tool to enable for prioritisation and deployment of resources and to drive risk-based decision-making:
- Provide customers capability outline their risk appetite frameworks including:
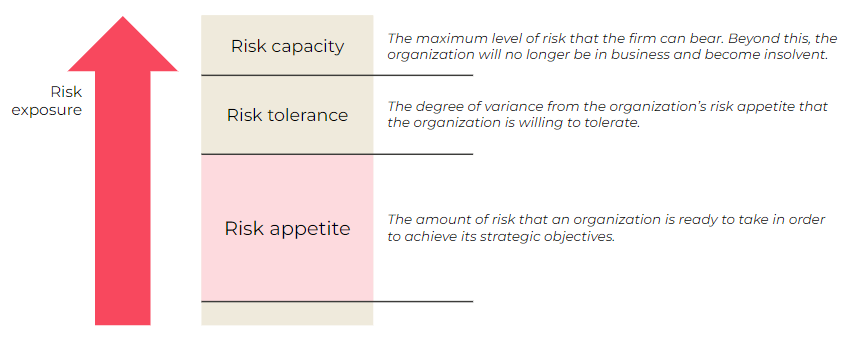
- Risk Appetite
- Risk Tolerance
- Improve the customer’s ability to understand their level of risk and how this aligned with the enterprise’s appetite for risk.
This will enable risk-based decision-making throughout the organisation:
- Ability to tailor the Risk Appetite framework and configure it as per the unique organisational needs and maturity in risk management.
- Ability to define the Risk Appetite, including documentation of qualitative Risk Appetite statements, Amber and Red thresholds for qualitative rating and loss expectancy and link it to the risk taxonomy.
- Ability to digitise the risk appetite breach management workflow to ensure subsequent actions are taken and risk is managed within the appetite.
- Monitor and track risk appetite effectively with automated alerts for non-adherence.
Customers identify and track Risk Appetite. They can tailor the Risk Appetite framework and configure it for their unique organisational needs and maturity in risk management.
They can define the risk appetite including documentation of qualitative Risk Appetite statements, Amber and Red thresholds (on the heatmap) for qualitative rating and loss expectancy and link it to the risk taxonomy.
The business outcome is to enable risk-based decision-making across organisations to meet strategic objectives. This enhancement is for mature risk organisations.
Industries such as financial services will find this very valuable.
4. Operational Resilience Workspace
The Utah release boosts the Operational Resilience Workspace with a new modern design, improved UX, and a configurable, persona-based workspace.
It helps with managing business services, importance and impact tolerance, scenario analysis and self-attestation tailored for Operational Resilience managers. Additionally, it includes a global navigation menu and a 360-degree view.
It allows customers to take advantage of the new updated UI and workspace for a holistic view of the resilience of their enterprise, to view and analyse any ‘red flags’ such as High Risks and Failed controls against their critical business services, and to manage all individual and team tasks from a single dashboard.
The business outcome is to improve visibility, drive efficiencies, and simplify navigation to strengthen the overall risk or compliance posture of the organisation.
Here are the details of the key Highlights of the Utah release:
Enhanced user experience for managing business services in the UIB workspace
This functionality will define service dependencies and collect resilience metrics:
- Auto-populate the dependencies from CSDM
- Auto-populate the dependencies from BCM – BIAs
- Define dependencies within operational resilience
- Track the risk, control, issues from the GRC applications
- Track the BC plans, exercises from the BCM application
- Track incidents, outages, vulnerabilities, change requests and tasks from IT workflow applications
- Visualise the resilience metrics
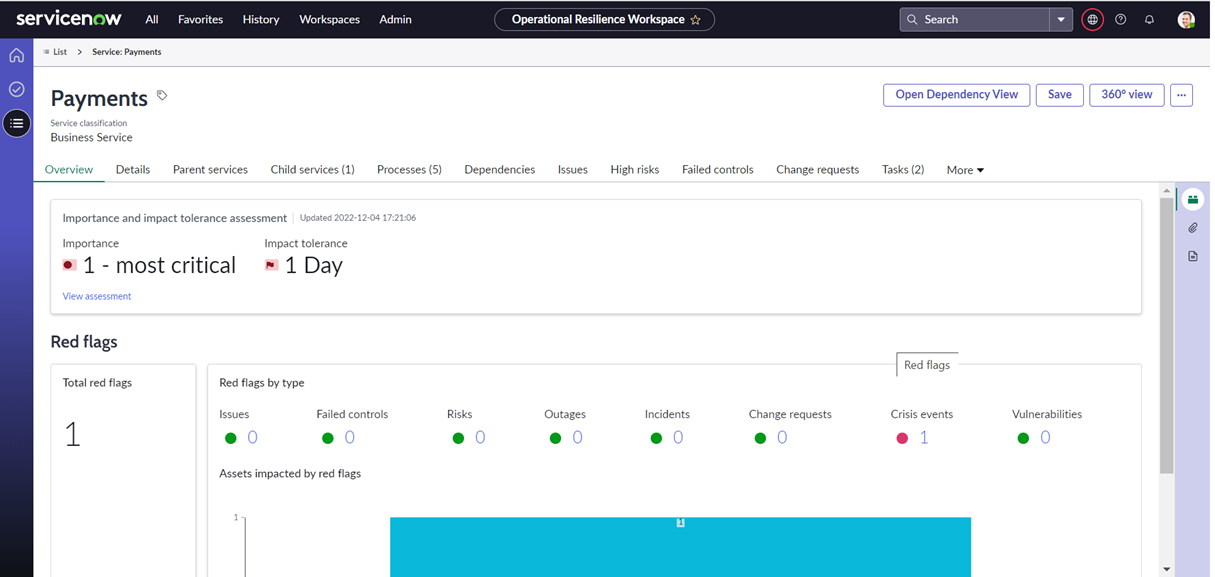
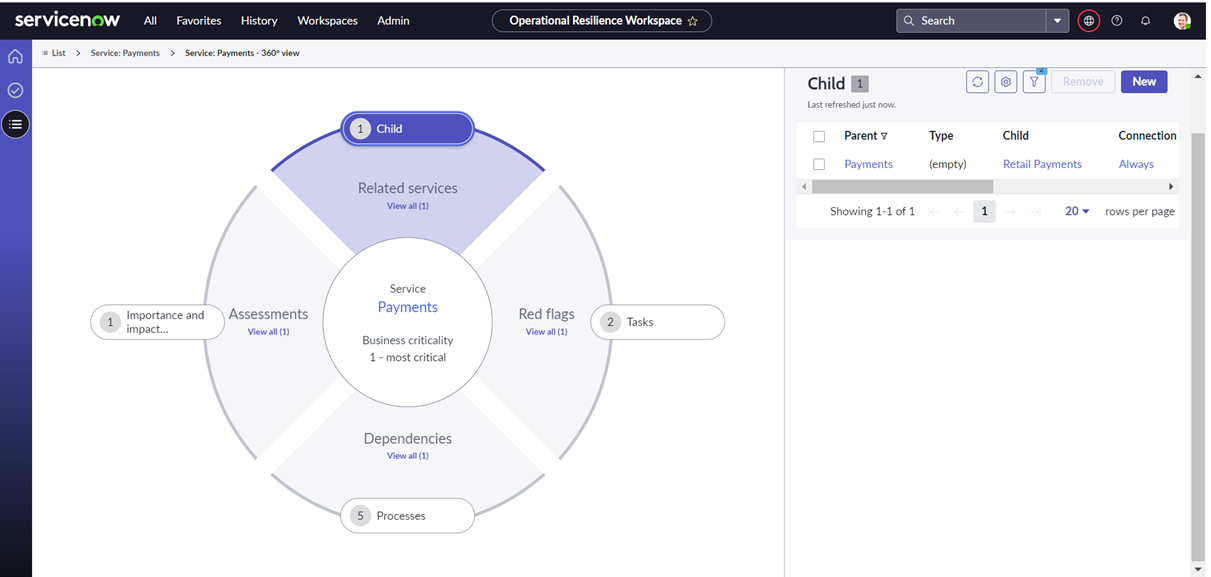
Get a holistic view of the business services – a 360-degree view
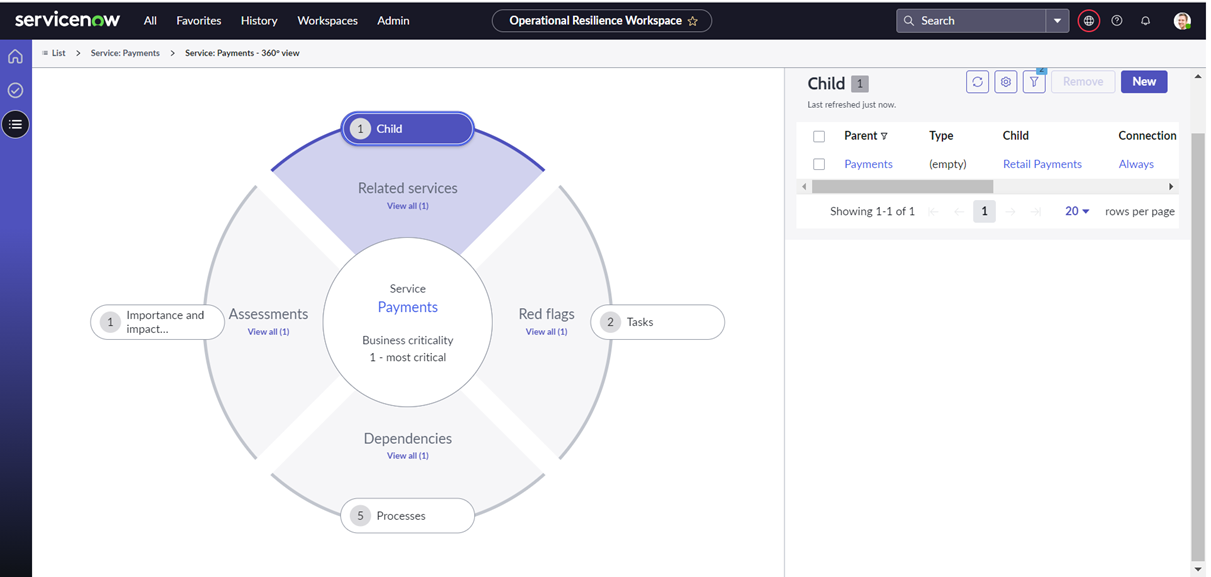
To help you to visualise the dependencies and resilience metrics:
- Visualise the parent and child services
- Visualise the process, technology, people, supplier and facility dependencies
- Visualise the resilience metrics
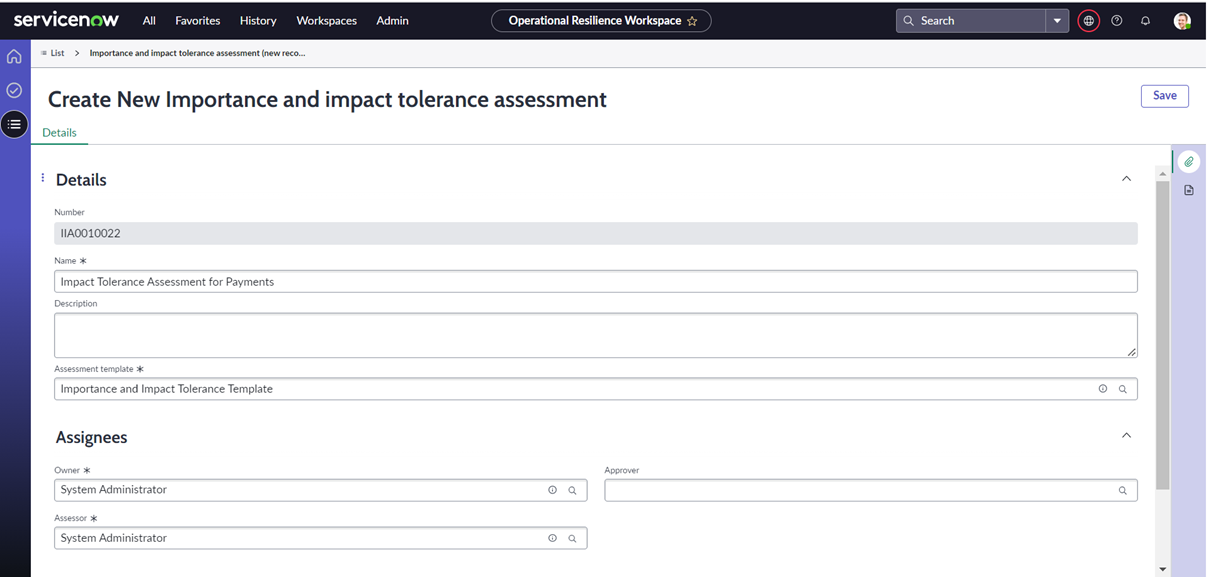
Enhanced user experience for managing importance and impact tolerance in UIB workspace
Through survey-based assessments for business services:
- Analyse the importance of the business services
- Analyse the impact tolerance of the business services
- Based on predefined survey templates
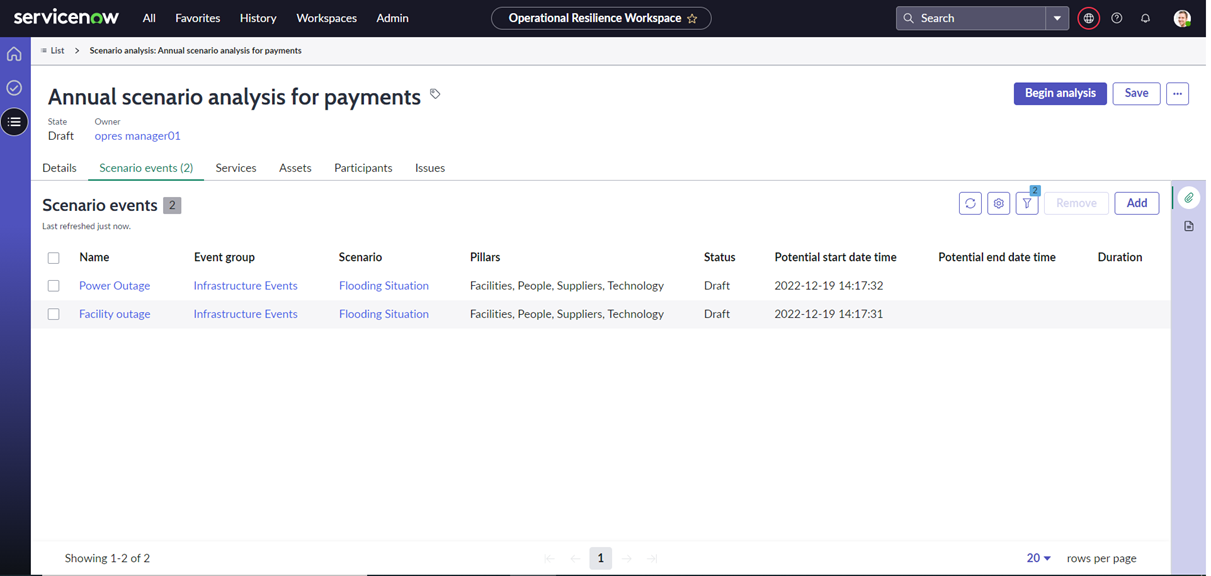
Enhanced user experience for managing scenario analysis in UIB workspace
You will be able to analyse the impact of scenarios and events on the business services, and track actions and improvements from the scenario analysis.
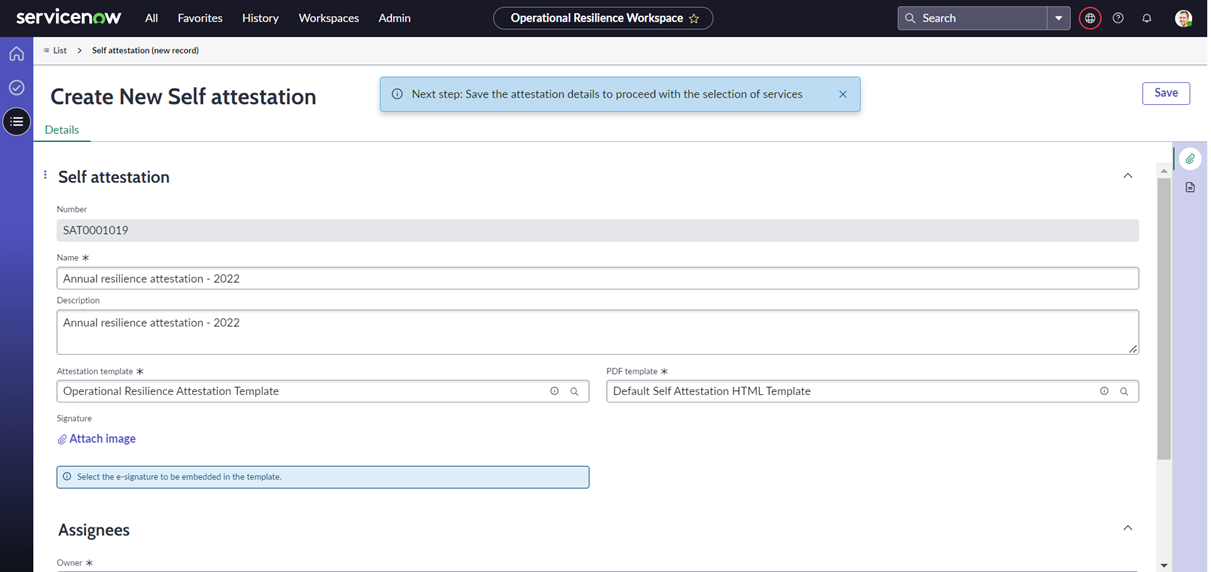
Enhanced user experience for managing self-attestation in UIB workspace
By generating PDF reports for resilience reporting based on predefined document templates.
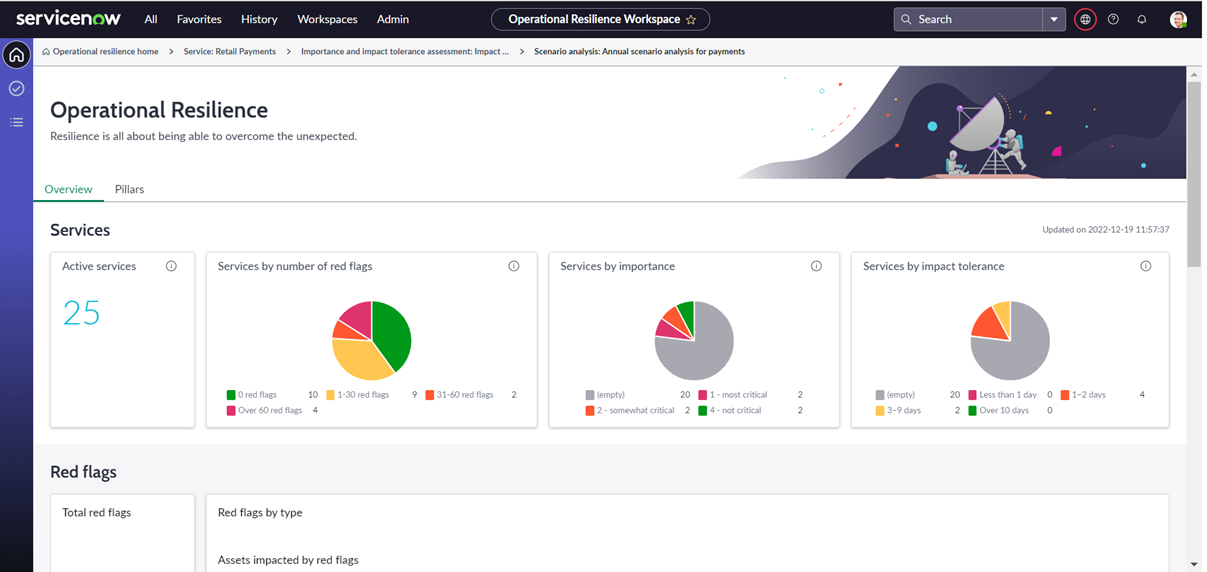
Get an overview of the operational resilience from the home pages
The new home page will show you the services resilience dashboard and the dependency pillars dashboards for resilience reporting.
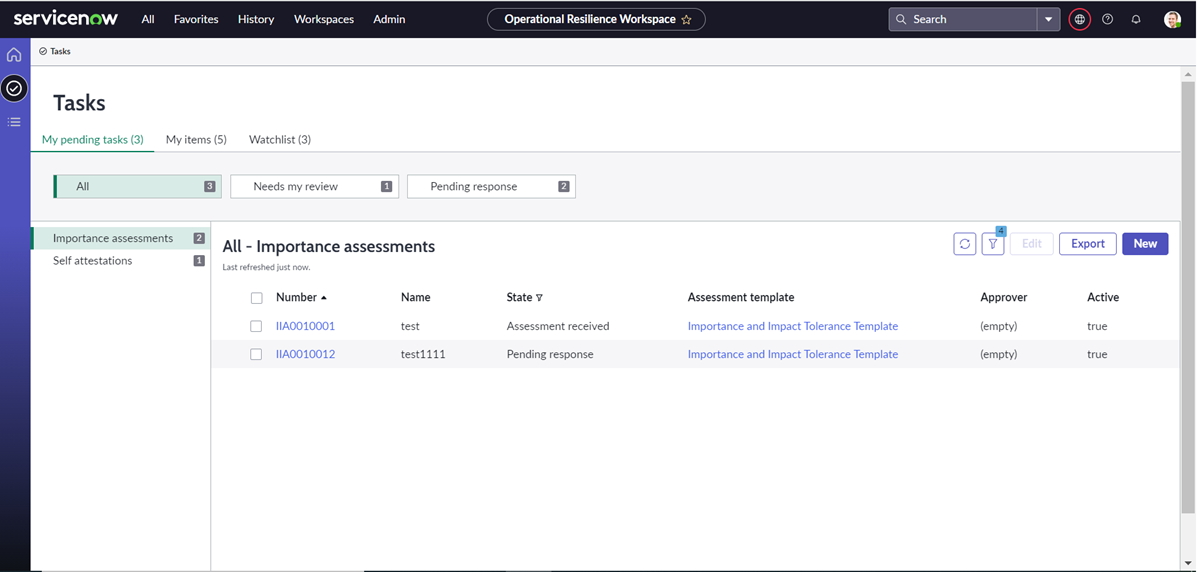
Manage individual and team tasks from a single dashboard – My Tasks
You will be able to track individual and team’s tasks from a single dashboard.